Institute of Cytology and Genetics;
United Institute of Geology, Geophysics and Mineralogy;
Institute of Chemical Kinetics and Combustion;
Institute of Inorganic Chemistry, SB RAS, Novosibirsk
Head of the Institute:
Vladimir K.Shumny, Academician of the RAS
10 Lavrentyeva Ave., Novosibirsk, 630090, Russia
Tel.: 33-35-26, Fax: 33-12-78,
email: schumny@bionet.nsc.ru
Principal researchers:
L.P.Osipova, Ph.D. (Biology), Senior researcher, Head of Sector, IC&G, SB RAS
K.P.Koutzenogii, Doctor of Sciences (Physics and Mathematics),
Professor, ICK&C, SB RAS
F.V.Sukhorukov, Ph.D. (Geology and Mineralogy),
Director assistant of the Analytical Center of United Institute of Geology, Geophysics and Mineralogy
Project objectives
Development of a model for complex estimation of the technogenic impact on environment, genofond and state of biological health of people.
High-latitude regions of Western Siberia are at present subjected to a powerful press of negative technogenic impact due to their strong oil-gas mastering and a number of other negative ecological factors including the consequences of nuclear tests on the Northern (Novozemelsk) testing ground.
The small number and long-lasting isolation of the indigenous population of the North predetermined their ecological sensitivity. Deterioration of the ecological situation has much effect particularly on these groups of the Siberian population and threatens their existence. Therefore, populations of scanty indigenous nationalities of the North and the regions of their settlement are a unique object for solving the above problem. One of the indigenous nationalities of the North is the Tundra Nentsi (Purovsk district of the Tiumen region, Yamalo-Nenets autonomous okrug). Solution of the problem suggests the development of research by two blocks:
- Deep population-genetic and molecular-genetic studies of the Tundra Nentsi population.
- Biospheric studies of the territory of the settlement of a given population. It is reasonable to distinguish the studies on the consequences of radionucleotide influence. This is determined by both particular hazard of these ecotoxicants and specific peculiarities of their behaviour in a trophic chain “soil-man”.
Background and significance of objectives
According to preliminary data, in the population of the Tundra Nentsi, the structure of the sickness rate has changed during the last decade: the cases of chronic, allergic and oncological deseases have increased in number. These facts indicate a decrease in the resistance of the immune system of indigenous population in changed conditions. Several cytogenetic studies of the Tundra Nentsi indicate a substantial increase (as compared with the background) in the number of rough chromosome aberrations. An analysis of general indices of blood indicate the characteristic changes typical earlier of the population of the regions affected by radiation. The unfavourable state of the biological status of this indigenous nationality of the North is, probably, related to various technogenic (global, regional, local) impacts which have a negative effect on the ecological situation in this region. The natural habitat of settled and nomadic settling of the Tundra Nentsi joins the Novozemel testing ground. There are data on the global and local deposition of 137Cs at these latitudes. A direct connection and close amount of caesium-137 have been established in lichens and deer meat which testifies to a constant inner irradiation of the indigenous population which mainly eats venison.
It is also important to obtain data on the levels of concentration of heavy metals (including toxic) and organic toxicants in different part of the environment. The region under study is situated in the zone of the exhausts of the giants of non-ferrous metallurgy (Norilsk, Kolsk Peninsula) and oil and gas-extractive and processing enterprises. Their influence on the environment and people health is reflected in the State report on the condition of nature in Russian Federation (1995).
Atmospheric processes determining aerosol transport (on local, regional and global scales) determine, as a rule, the levels of pollution of all parts of biosphere by the most dangerous ecotoxicants such as radionucleotides, cancerogens, pesticides, heavy metals. Atmospheric aerosols and physico-chemical heterogeneous processes fully determine the chemical composition of precipitation and often the chemical and ionic compositions of surface waters. For a given region, precipitates are the main source of drinking water as well as the medium for fish being one of the basic products of the indigenous population.
Preliminary studies of the ionic composition of atmospheric aerosols, snow falls and surface waters of the region show that at small mineralisation of river and lake waters there are reasons for the manifestation of the effect of “acid” rains. It is known that the negative effects of “acid rains” observed in some northern regions of the world, lead to the increased migration of heavy metals in terrestrial and water ecosystems and distortions of their functioning up to complete degradation.
Research plan: approaches and methods
The organised body of executors has:
- the basic equipment and reagents for biochemical, cytogenetic, immunologic and molecular-genetic studies;
- contemporary methods and equipment for selecting aerosol, soil, vegetation and water samples and precipitates;
- contemporary analytical basis for performing complex analysis of the chemical composition of the objects of the environment (nuclear-physical, spectroscopic, chromatographic, and chromato-mass-spectrometric);
- contemporary methods of mathematical modelling, planning and processing of experimental data and up-to-date computers.
Expected results
For the first bloc, we shall estimate the biological status of the population of the Tundra Nentsi, analyse the variability of a wide range of genetic blood markers, perform a deep cytogenetic study of chromosomes to reveal various chromosome aberrations, estimate the level of mutability of a series of DNC sections.
For the second block, we shall reveal the levels of natural and artificial long-living raduonucleotides in components of biogeocoenosis and the main foodstuffs of the Tundra Nentsi, perform a complex study of the regional factors of formation of surface waters and atmospheric components, reveal the main sources of contamination in the region and their types, determine the regularities of migration of ecotoxicants, create the database on radioactive contamination of soil and peatbogs by 137Cs and 90Sr for retrospective estimation of dose loadings including internal irradiation via the chain “reindeer moss-deer-person”.
The results obtained will lay grounds for a dedicated database. A monograph will be written.
List of publications of participants related to the project
Thirty five papers have been published on the problem suggested. The main papers are as follows:
-
Osipova L.P., Posukh O.L., Ivakin E.A., Kryukov Yu.A., Karafet T.M. Genofond of indigeneous population of Samburg tundra // Genetika. – 1996. – Vol. 32, ą 6. – P. 830-836.
-
Posukh O.L., Osipova L.P., Krukov Yu.A., Ivakin E.A. Genetic and demographic analysis of indigeneous population of Samburg tundra // Genetika. – 1996. – Vol. 32, ą 6. – P. 822-829.
-
Osipova L.P., Posukh O.L., Kutsenogii K.P. et al. Epidemiological studies for the assessment of risks from environmental radiation on Tundra Nentsi population // NATO ARW Workshop Fundamentals for the assessment of risks from environmental radiation, 6-10 October, 1997, Brno, Chech Republic.
-
Osipova L.P., Posukh O.L., Matveeva V.G., Ponomareva A.V., Sukhorukov F.V., Shcherbov B.L., Strakhovenko V.D., Koutzenogii K.P., Raputa V.F., Smolyakov B.S., Rivin G.S., Klimova E.G. Complex estimation of technogenic impact on genofond and biological human health (tundra Nentsi) // Integration programs of fundamental research. Novosibirsk: SB EAS, 1998. – P. 327-342.
-
Osipova L.P., Posukh O.L., Koutzenogii K.P., Sukhorukov F.V., Matveeva V.G., Grafodatskii A.S., Konovalova N.A., Sukhovey Y.G., Petrov S.A., Lefranc G., Lefranc M.-P. Epidemiological studies for the assessment of risks from environmental radiation on Tundra Nentsi population // NATO Science Series. Series 2: Environmental Security. Fundamentals for the assessment of risks from environmental radiation. – 1999. – Vol. 55. – P. 35-42.
-
Shore R.E., Osipova L.P., Atwell W., Erees F.S., Fry R.J.M., Ivanov V.K., Khanh T.Q., Knuschke P., Komochkov M.M., Quastel M.R., Tomasek L., Tyrrell R.M., Bjorn L.O., De Gruijl F.R., Greinert R., Obe G., Rettberg P. Risk assessment // NATO Science Series. Series 2: Environmental Security. Fundamentals for the assessment of risks from environmental radiation. – 1999. – Vol. 55. – P. 81-90.
-
Osipova L.P., Posukh O.L., Ponomareva A.V., Sablina O.V., Perelman P.L., Shcherbov B.L., Strakhovenko V.D., Sukhorukov F.V., Koutzenogii K.P., Matveeva V.G., Rivin G.S., Smolyakov B.S. Environment and its influence on human genofond: experience of complex studies // Vestnik VOGiS. – 1999. – ą 8. – P. 11-16. (In Russ.).
-
Koutzenogii P.K., Van Malderen H., Hoornaert S., Van Grieken R., Koutzenogii K.P., Bufetov N.S., Makarov V.I., Smolyakov B.S., Nemirovskii A.M., Osipova L.P., Kryukov Yu.A., Ivakin E.A., Posukh O.L., Bronshtein E.L. Siberian haze. Complex research of Siberian aerosols // Optika atmosfery. – 1996. – Vol. 9, ą 6. – P. 712-719. (In Russ.).
-
Koutzenogii K.P., Bufetov N.S., Ivakin E.A., Kryukov Yu.A., Konovalova N.A., Osipova L.P., Posukh O.L., Taraskina A.I. The potentialities of SRXRF technique in analyzing a technogenic impact on northern population // Theses of Republic conference “Regional nature management and ecological monitoring”. Barnaul, 27-29 September. – P. 107-109.
-
Koutzenogii K.P., Osipova L.P., Posukh O.L., Bufetov N.S., Smirnova A.I., Kryukov Yu.A., Ivakin E.A., Konovalova N.A. The potentialities of SRXRF technique in analyzing a technogenic impact on northern population // Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research. –1997. – P. 30-36.
-
Shcherbov B.L., Strakhovenko V.D., Osipova L.P., Posukh O.L. Cezium-137 in moss and ichen as an in dex of radioactive contamination of Western Siberia // Proc. of Scientific Conference “Actual problems of geology and geography of Siberia”. Tomsk, 1998. – Vol. 3. – P. 302-304.
-
Shcherbov B.L., Osipova L.P., Strakhovenko V.D., Posukh O.L. Signs of technogenic impact on biogenocenosis in settlements of tundra Nentsi // Proceedings of Scientific Conference “Crisis and precrisis of the environment as a result of technogenic impact on geological medium and geomorphosphere”. Lvov, 1998. – P. 5-6.
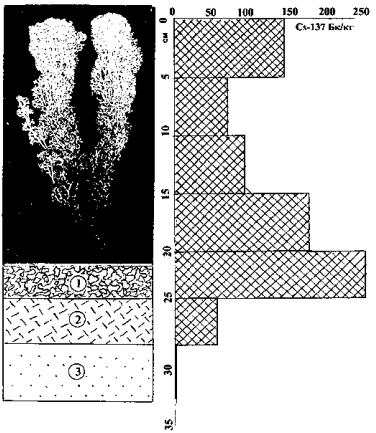
Fig. 1. Vertical distribution of Cs-137 in the profile of reindeer moss-soil at site N.67.
1-deteriorated rotten reindeer moss; 2-forest bedding; 3-sand.
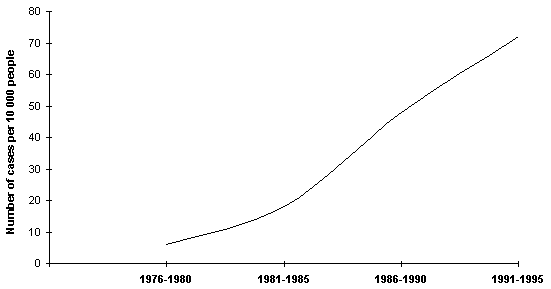
Fig. 2. Growth of mortality because of oncologic deseases in the population of the settlement of Samburg.
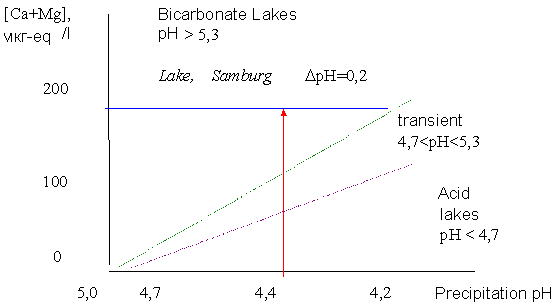
A nomogram for predicting changes in lake pH with increased acidity of precipitates.