Institute of Biophysics, SB RAS, Krasnoyarsk
Head of the Institute:
Andrey G.Degermendzhy, Doctor of Physical and Mathematics Sciences
Akademgorodok, Krasnoyarsk, 660036, Russia
Telephone: 7(3912)43-15-79
Telefax: 7(3912)43-34-00
email: ibp@ibp.krasnoyarsk.su,
degbol@intra.krasnoyarsk.su
Principal researchers:
L.G.Kosolapova, Ph.D. senior researcher
A.Ya.Bolsunovsky, Ph.D., senior researcher
V.M.Belolipetsky, Doctor of Science
Project objectives
The project objective is to develop a tool (Environmental Decision Support System) to evaluate and predict the radioecological consequences of artificial contamination of the Yenissei Rriver. The tool – a mathematical model – is of generic character and applicable to other objects. The Mining-Chemical Works (MCW) (Ministry of the Nuclear Power Industry of the Russian Federation) in Zheleznogorsk (Krasnoyarsk-26), one of the world largest facilities for producing military plutonium, has been in operation in the Krasnoyarsk Kray since 1958. Working for many years, the reactor and radiochemical production have contaminated more than one thousand kilometres of the Yenissei River, the flood plains, and adjoining areas with artificial radionuclids, including transuranium elements. Storage facilities on the territory of the works, in aquifers amassed tremendous amounts of radioactive wastes with a total activity of more than one billion Curie. Accidental releases of radionuclids into the environment and the Yenissei River can contaminate not only close surroundings of the Krasnoyarsk Kray, but also the Kara sea of the Arctic ocean. Until 1991 the radioecolgical situation of Yenissei was monitored by the agencies of the Ministry of the Nuclear Power Industry only. Democratisation processes in Russia and the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant accident, in particular, facilitated the development of independent radioecological research. However, the actual extent of the radioactive contamination is still subject to research (transuranium elements, in particular). The Yenissei river flood plains are a convenient test object to investigate the long-term effects of prolonged radioactive contamination of a large river system. The world community is interested in increasing scientific knowledge by understanding the parameters involved in radionuclid transport/redistribution along river systems, and in developing methods to evaluate and predict radioecological consequences of prolonged contamination of a river, in particular by long-life transuranium radionuclids.
Background and significance of objectives
- To develop a package of mathematical models describing hydro-physical and biological mechanisms of radionuclid migration in river system components.
- To develop methods to evaluate radionuclid inventory in soil and bottom sediments, and methods to define transfer coefficients and fluxes of radioisotope from flood plain soil and bottom sediments.
- To evaluate experimental coefficients of radionuclid uptake by hydrobionts present in the Yenissei River.
- To define a minimum set of ecological parameters to allow an efficient evaluation and prediction of the radioecological status of the river.
- To derive and recommend efficient and social-economically acceptable measures for rehabilitation.
- To evaluate contribution of suspended matter and biomass of hydrobionts into space-time distribution of radionuclids over the river system components (mathematical model experimentation).
- To develop an Environmental Decision Support System to define parameters capable of improving the radiation situation and provide strategies for remediation/rehabilitation in the Yenissei river flood plain.
Research plan: approaches and methods
Investigations of migration processes, concentration and biological effects of radionuclids in living and abiotic components of the river system. Development of generic principles to describe the migration of radioactive isotopes in aqueous ecosystems. Definition of ecological standards of anthropogenic load on water biocoenoses. Theoretical basics of mathematical modelling of radionuclid migration in water bodies have been developed by the research team (Kryshev I.I., Sazykina T.G.) of the Radium Institute (St.-Petersburg), experimental investigation of radionuclid migration over trophic chains in a water ecosystem has been made by Gennady G. Polikarpov of the A.O. Kovalevsky Institute of Biology of Southern Seas (Sevastopol) for marine water bodies, and Kulikov N.V. and Chebotina M.Ya. of the Institute of Plant and Animal Ecology (Russian Academy of Sciences, Urals Branch) in Yekaterinburg for fresh-water bodies.
List of publications of participants related to the project
-
Degermendzhy A.G., Kosolapova L.G. Development of Prognostic Model of Radioecological State of the Yenissei River // Proceeding of the International Conference on Probabilistic Safety Assessment: Methodology and Applications, Korea, Seoul, 1995. – Vol. 1. – P. 527-531.
-
Degermendzhy A.G., Kosolapova L.G., Belolipetsky V.M. A prognostic model of radioecological status of the Yenisei River // Procs. of the International Symposium “Hydrological and Ecological Processes in Water Bodies and their Basins. Novosibirsk, Sept. 26-28, 1995. – P. 85-86.
-
Degermendzhy A.G., Shevyrnogov A.P., Kosolapova L.G., Levin L.A., Chernousov A.V. and Vlasik P.V. “New Ecological Mechanism of Formation of Spatial Distribution of Radionuclids in River Ecosystem” // Proceedings of the International Conference on Deep Geological Disposal of Radioactive Waste. Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada, 1996 September 16-19. – Vol. 4. – P. 27-36.
-
Degermendzhy A.G., Kosolapova L.G., Vlasik P.V. Theory, Computational Method and Software for Prognosis of Migration and Distribution of Radioactive Matters in River Ecosystem // Proceedings of XI International Conference on Computational Methods in Water Resources. Volume 2: Computational Methods in Surface Flow and Transport Problems. Cancun, Mexico, 1996 July 22-26. – P. 277-284.
-
Degermendzhy A.G., Kosolapova L.G., Belolipetsky V.M. Mathematical Modelling of the Dynamics of Radioecological and Hyrdophysical Features of River Systems (Yenisei) // Sib. Ekol. Zhurnal. – 1996. – ą 5. – P. 473-484.
-
Degermendzhy A.G., Kosolapova L.G. A Mathematical Model of the Ecological Mechanism of Heterogeneity of radionuclid distribution in the river system water-phytoplankton-zooplankton-sediments // DAN. – 1997. – Vol. 354, ą 1. – P. 131-134.
-
Degermendzhy A.G., Kosolapova L.G. Mathematical Theory of New Ecological Mechanism of Formation of Spatial Distribution of Radionuclids in River Ecosystem // Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Data for Science and Technology. Italy, Trieste, 1997, May 19-24. – Vol. 59, Part 2. – P. 1373-1376.
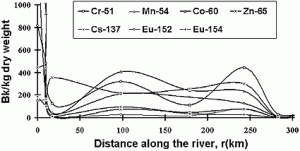
Fig. 1. Distribution of radionuclides along the Yenisei river from radioactive waste discharge site.