Institute of Computational Mathematics and Mathematical Geophysics, SB RAS, Novosibirsk
Head of the Institute:
Boris G.Mikhailenko, Doctor of Physical and Mathematics Sciences, Professor
6 Lavrentyeva Ave., Novosibirsk, 630090, Russia
Tel: (383-2)-34-33-53, Fax: 32-42-59,
email: mikh@sscc.ru
Principal researchers:
G.N.Erokhin, Doctor of Physical and Mathematics Sciences, Professor
Project objectives
The purpose of the project is the creation of a system of operating space monitoring of the environment of Siberia, and also databases of complex monitoring and means of network access to them.
The basis of the project is the use of technologies of space sounding and complex monitoring of territory of Siberia for solving the problem of objective environment control of Siberia (climatic and ecological control, forecast in the territory of regions of the conditions of soil and vegetative covers, bogs, wood and water resources, glaciers, forecast freshet and channel processes, monitoring of continental water, marine and coast environment), and also determination of coordinates, prediction of extreme phenomena and situations (wood fires, splashing down of territory, propagation of the wreckers of a wood, occurrence and development of landslips etc.). The important feature is the use of the operating information from Russian and foreign satellites, modern geoinformation systems and methods of processing of space images, theme decoding on the basis of a network of ground stations for receiving satellite information in Siberia
The project will promote problem solving under the analysis and forecasting of dynamics of the development of the Siberian region, search of the rational administrative solutions on development of natural and economic resources of the region of Siberia in view of ecological, economic and social factors, and also get decide on recommendations on protection of the environment.
Background and significance of objectives
The learning of natural resources of the Earth and forecast of disastrous processes by remote sounding instruments on satellites and aircraft, is one from heavily developing directions of a science and engineering. Complexity of problems of interaction of the man and nature increasing scales of anthropogenic effect on an environment, necessity of rational use of natural resources and the obtaining of necessary useful production without pernicious effect on the nature, make this direction especially urgent. The remote sounding provides unique capabilities of operating data acquisition on a global scale with the high spatial, spectral and temporary sanction. It is especially urgent for Siberia, of which the territory is vast, and the network of data acquisition is non-uniform, does not cover the territory entirely and does not take into account all variety of the data, necessary for analysis.
The promising information technologies in applied remote research of the Earth from space in the coming years will associated with the network GIS-technologies oriented to problem solving of the users, space images, connected to automated processing.
The necessity in geoinformation technologies is determined by a vital necessity of effective storage of the geoinformation, taking into account volumes of the stored and processed geodata, and also remote access to them, through global computer networks. The urgency of the creation of geoinformation banks and uses of new effective technologies of access to them is reinforced in the present situation in Russia also by high costs of obtaining of new information and, on the other hand, threat of irrevocable loss of the available geoinformation in conditions of continuously worsening financial capabilities of organizations ñ holders of the geoinformation.
The spectrum of possible appendices of geoinformation systems is extremely wide – on the basis of GIS the development of various appendices for land-survey problems (ground land-survey, land-survey of the engineering communications etc.), ecological problems (ecological monitoring, ecological cartography etc.), problems of rational nature using, theme cartography, various geological appendices, problems of management of the information about buildings and facilities, problems of operating control by municipal economy etc. are conducted.
The efficiency of use of geoinformation systems justifies all consumption associated with their creation or gain.
Taking into account large flows of satellite information, necessity of processing high-resolution and large-dimension data (multispectral shooting from space), it is necessary to actuate in a network(grid) of rather high-power servers, such as a supercomputer centre created on the basis of ICM&MG.
ICM&MG (the former Computing Center) has a significant scientific and practical backlog under the offered project.
In 1978 Center of processing of the geoinformation (CPGI) was organised in the Computing Center.
The main scientific direction of CPGI is automation of processing of the space images, mainly, in the interests of SB RAS Institutes. During 19 years the information received from orbital stations, planes – laboratories and ground data was used by CPGI together with SB RAS institutes, the Western Siberian Regional Centre of Satellite Data Acquisition and Processing (Western Siberian RCRPSD), and also with a number of organisations of various departments for the solution of a lot of applied problems. In particular, algorithms and software for allocation on the space images of linear and ring-type structures are created. This complex of programs was productively used for processing of space snapshots of the eastern part of the Siberian platform (Yakutia). The same complex of the programs was used in automated processing of space snapshots of the territory of Northern Armenia within the framework of complex research of region Spitak earthquake. The new results updating a structure of the Spitak earthquake were obtained qualitatively.
Together with the Western Siberian RCRPSD, both the Sukachev Institute of Forest, SB RAS (Krasnoyarsk), the direct channel of satellite data transmission for solving the problem of operating detection of the centres of wood fires on phone lines of communication was organised. However, this communication channel has proven technologically unprofitable because of a low speed and reliability of data transfer.
Since 1982 in the department of image processing of the Computing Center, SB RAS, the developments of GIS subsystems for solving the problem of the Russian topographical service on processing of digital information about the district, and also for problems of operating control by urban region are conducted. The complex “Editor” intended for the control and editing of digital cards to district, was adopted in 1990 in the Soviet Army by the order the ministry of defence.
Now within the framework of the creation of a collective Center of Supercalculations in CM&MG, SB RAS, a modern information network including more than 200 computers, working under operational systems Windows, OS/2 and UNIX (various versions) and linked to the global network Internet is created. The computer center is putting in operation the supercomputer RM-600 E30 of the Siemens corporation with up to 4 billions of operations per second and with the main memory 4 Gigabytes. Besides, the network computing POWER CHALLENGE M server, with the peak performance 300 MGFlops (the analogue CRAY YMP) supports operation in the Internet of several databases with the use a DBMS Informix ( http://sgi.sscc.ru/informix/ ). In the ICM&MG, SB RAS, a number of WWW-servers (www.sscc.ru, www-gis.sscc.ru, omzg.sscc.ru, osmf.sscc.ru) are created, and also access to GIS-servers ICM&MG ( http://irix.sscc.ru/grasslinks/, http://www-gis.sscc.ru/grasslinks/ ) with on-line access, that has no analogues not only in Siberia, but also in Russia.
ICM&MG actively cooperates with the Western Siberian Regional Centre of Satellite Data Acquisition and Processing (West Siberian RCRPSD) in Novosibirsk. The Western Siberian RCRPSD is one of three large centres in Russia acquiring, preprocessing and distributing satellite data on space systems natural resource, oceangraphical and meteorologic directions. These data are used in interests of hydrometeorology, geophysical service, system of warning about acts of nature and extreme situations, services of the ecological control, maintenance of scientific researches on a broad circle of problems of a condition of an environment.
The West Siberian RCRPSD receives operating information of small, mean and high resolution from artificial monitoring-exploratory and meteorological satellites of ground on the territory of Siberia and Central Asia. The activity of the Center simultaneously with the space systems “Meteor-2”, “Meteor-3”, “ocean – about”, “resource – about”, “NOAA” enables the consumers to combine different kinds of the information depending on onboard devices (scanners, telephotometers, spectrometers, radiometers, radars) and spectral ranges (visible, near, mean and distant infrared)). Rather broad the selection of the spatial resolution of the received data is: from 4 km. On district for meteorological information up to 45 m for monitoring-exploratory data. The information is written on the COMPUTER and the preprocessing is performed, if necessary.
The West Siberian RCRPSD acquire information with foreign satellites, giving the data of a local scale since the last 10-17 years. In questions of practical use of remote sounding the main accent is done on space on monitoring of the wood arrays and agricultural crops, and also on ecological, geological, geographical applications. The methods of simulation of the Earth as difficult system based use of global space monitoring are being developed.
The main ecological problems of Siberia are connected that at mastering of power and raw base the ecological requirements were admitted excessive, while the funding of nature preservation quite modest, mastered only partially, not complex and superficial use of raw material resulted in large losses of wood, metals, passing gas, gaseous condensation and other valuable products. All this was accompanied by significant violations and pollution of natural environment on a background of climatic features of region, limiting ability ecosystem to selfrecovery.
The analysis of an ecological situation in territory of Siberia shows, that practically in all subjects of Federation of region there are zones of ecological trouble. To them, first of all, industrial centres of Siberia and the solution of ecological problems with the purposes of regulation of prime costs on rehabilitation ecological . of unsuccessful territories.
The learning of natural resources of the Earth and forecast of disastrous processes with the help of instrumentation of remote sounding placed on satellites and aircraft, is one from heavily developing directions of a science and engineering. Complexity of problems of interaction of the man and nature increasing scales of antropogeneous effect on an environment, necessity of rational use of natural resources and the obtainings of necessary useful production without pernicious effect on a nature, do(make) this direction especially urgent.
The remote sounding of the Earth sounding provides unique capabilities of operating data acquisition on a global scale with the high spatial, spectral and temporary sanction. It is especially urgent for Siberia, which regions take the huge spaces, and the network of data acquisition is non-uniform, does not surround all territory and does not take into account all variety of the data, necessary for the analysis.
Research plan: approaches and methods
For the solution of the above problems, the maximum broad spectrum of Russian and foreign means of remote sensing will be used:
- wide-form scanners of the mean resolution “RESURS-Œ1” MSU-SK (160 m);
- all-weather radar scanners of the ERS class;
- scanners of the high resolution, the MSU-E (40 m), “RESURS-Œ1” satellite;
- scanners of the high resolution, (10-20 m), the “SPOT” satellite;
- the perspective information technologies in application remote researches of the Earth from space will be connected to network GIS-technologies oriented to problem solving of the users, space images, connected to automated processing.
The necessity in geoinformation technologies is determined by vital necessity of effective storage of the geoinformation, taking into account volumes of the stored and processed geodata, and also remote access to them. The urgency of creation of geoinformation banks and uses of new effective technologies of access to them is reinforced in a present situation in Russia also by high costs of obtaining of the new information and, on the other hand, threat of irrevocable loss of the available geoinformation in conditions of continuously worsening financial capabilities of organizations – holders of the geoinformation.
Expected results
The databases of space monitoring of an environment of Siberia, means of processing of space snapshots will be developed of the accompanying information and the module of decision making and is supplied access to these databases through Internet.
Main result of implementation of the program will be increase of efficiency of problem solving on protection and savings of natural resources of regions of Siberia, switching:
- The operating control of an ecological condition of an environment in regions of Petroleum and gas deposits and developments of hard minerals, Oil pipeline, with detection of large industrial lets and resets of polluting substances in atmosphere and water objects.
- Ecological monitoring of a condition of taiga territories, control behind a condition of the salted territories and bog derivation processes.
- Operating assessment and forecast of change of a regional condition of natural resources under effect of natural and antropogeneous processes for expert assessments of a condition ambient.
- Assessment of a condition of water and snow resources.
- Derivation of avalanches, glaciers, including dynamics and forecast of a mode of a drain of the rivers.
- Ecology and economic classification of grounds and their monitoring.
- Structuring of the sowing areas of region, control of erosion of processes, dynamic cartography of the sowing areas and wood arrays on temperature and humidity, control and assessment of the index of vegetative covers, including reindeer pastures of forest tundra, control and assessment of dynamics of zones of a drought (dynamic cartography of territory of Siberia on fire dangerous zones).
- Assessment of a condition agricultural lands for the purposes of forecasting(prediction) of crops.
- Regional nature environment control and nature environment using on the basis of the operating space information of the high resolution.
- Operating assessment and control of vegetative and soil covers, condition of the wood arrays (for the purposes of detection wood pathology and development of new technologies of wood cultivation and wood maintenance).
- Organization of a system continuous wood control on the basis of the space information of the high resolution.
- The operating control and forecast of a condition of the hunting resources.
- The operating detection and topographical binding with accuracy is not worse 1 km of occurrence of wood fires with the forecast of dynamics of their development.
- Detection and tracking mass propagation of the wreckers of a wood.
- Operating assessment and control of vegetative and soil covers, condition of the wood arrays, zones of cuttings down and dynamics of their recovery.
- Operating detection, determination of coordinates and forecast of development of wood fires, propagation of the wreckers of a wood.
- The operating control thunder-storm danger of atmospheric derivations.
- Information maintenance of development of regional technologies of protection and protection of woods.
- Increase of efficiency and reliability of forecasting, assessment of extreme situations of a natural and anthropogenic origin with the dynamic forecast and their development in inspected territory.
- The control for abrasion of a coast line of the large rivers in region of the occupied items and other economic objects.
- The operating forecast of a condition of a water mode of the rivers of Siberia with use of the ground and satellite information.
- The control behind atmospheric carry of pollution and information maintenance of models of the forecast of distribution technogenic releases in atmosphere.
List of publications of participants related to the project
-
Alekseev A.S., Erokhin G.N. On creation of Siberian Center of Supercalculations // Information technologies and computing systems. ñ 1997. ñ π 2. ñ P. 1-11.
-
Alekseev A.S., Erokhin G.N., Fedotov A.M., Shokin Yu.I. Network geoinformation technologies in SB of RAS // Information technologies and computing systems. ñ 1997. ñ π 2. ñ P. 33-42.
-
Alekseev A.S., Erokhin G.N., Kopylov V.N. About creation of centre of space monitoring in Siberia // Materials the Second scientific Conference “Intellectual automated systems in control”, Novosibirsk, April 15-16. ñ 1997.
-
Erokhin G.N., Kopylov V.N. On creation of Center of space monitoring of natural resources and processes of Siberia // Proceedings of scientific seminar of the users nature resource and oceangraphic space data. ñ Moscow, October 27-29 1997. ñ P. 44-45.
-
Alekseev A.S., Erokhin G.N., Zinenko V.I., Kopylov V.N., Zatsepin A.G., Korotkevitch M.N. Remote space methods of monitoring of an environment in Siberia // Theses of the international exhibition – conference “Natural resources of the countries of CIS “, St.-Petersburg, November 1998. ñ P. 37-40.
-
Erokhin G.N., Zabadaev I.S., Kuznetsov V.L., Marchuk A.G., Ponomarenko M.P. Development program – information of maintenance for realization of multydisciplinary researche on the basis of high-efficiency computers // Intergrated program of fundamental researches. ñ Novosibirsk, 1998. ñ P. 159-173.
-
Alekseev A.S., Erokhin G.N., Mainagashev S.M., Tetenov E.V., Zinenko V.I., Kopylov V.N. Space monitoring of an environment in Siberia // Theses of the report on an international symposium of the control and rehabilitation of an environment. June 17-19 1998, Tomsk. ñ P. 39-40.
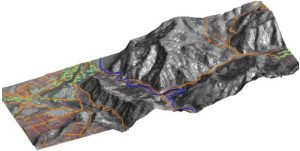
Fig. 1. 3D the image of region Aizu (Japan) combined with vectorial layers of the rivers, roads, urban constructions. The snapshot of the chamber of the high resolution (2 m) KBP-1000, series, established on satellites, “Kosmos” is used.
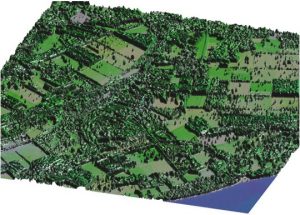
Fig. 2. 3D representation RGB of the image from a satellite SPOT. Region of Krasnoobsk, Novosibirsk area. As altitude the values of the vegetation index NDVI, calculated on RGB to the image are used. The algorithm of calculation of an vegetation index allows to recognize presence of vegetation and to estimate its weight.
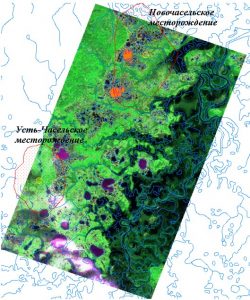
Fig. 3. The processed image of region of mean current of the Taz River obtained with a satellite RESURS-O1 No. 3. The resolution 40 m. The orange colour allocated anomalies of reflecting ability of lakes. It is visible, that these anomalies are located in regions of deposits of gas, boundarying by the geologists. The explanation of the reasons of such anomalies requires additional researches of an ecology of lake, and also physical and chemical properties of a water.
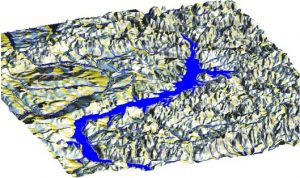
Fig. 4. 3D representation of digital model of a relief of region of Krasnoyarsk reservoir. On the image the vectorial layers of the rivers and water pools are put.
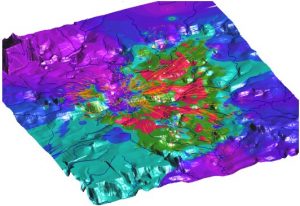
Fig. 5. 3D representation of estimated amplitude of a shock wave of the Tunguska explosion (the Tunguska River, 1908). On the image the vectorial layers of the rivers and directions fallings of a wood are put. This natural catastrophe of a unknown nature has taken place in 1908 in Evenkiya (Eastern Siberia, the Tunguska River region). The Tunguska explosion of 20 Megatons TNT equivalent made trees fall outward in a radial pattern over an area of 2,150 square kilometers. Using the data on fallen wood (distribution of trunks of trees on a direction of a falling) the renovation of the distribution of a shock wave of the Tunguska explosion was carried out. The center of explosion and anisotropy of power of a shock wave on a direction is precisely seen. More in detail see http://omzg.sscc.ru/.