Institute for Water and Environmental Problems, SB RAS, Barnaul
Head of the Institute:
Yuri I.Vinokurov, Doctor of Geographical Sciences, Professor
105 Papanintsev St., Barnaul, 656099, Russia
Office telephone: 8-3852-367-855
Fax: 8-3852-240-396
email: Iwep@iwepsb.altai.su
Principal researchers:
Œ.F.Vasiliev, Academician,
Institute for Water and Environmental Problems
I.I.Kiknadze, D.Sci.
Institute of Cytology and Genetics
V.D.Gulayev, Ph.D.
Institute of Systematization and Animal Ecology
V.V.Kirillov, Ph.D.
Institute for Water and Environmental Problems
“.S.Papina, Ph.D.
Institute for Water and Environmental Problems
¿.S.Khabidov, Ph.D.
Institute for Water and Environmental Problems
S.L.Shirokova, Ph.D.
Institute for Water and Environmental Problems
Project objectives
Studying of the biological diversity of the Œb River basin and Œb-Irtish interfluvial area aquatic ecosystems at genetic, species, population and ecosystem levels. The ecotoxicological estimation of water objects by methods of bioindication and biotesting on the basis of biochemical, cytogenetical, physiological and ecological characteristics of biological systems of various organisation levels.
Background and significance of objectives
The choice of scientific goals in studying of the Siberian aquatic ecosystem is determined by the necessity of solving the fundamental scientific problem on establishment of a relative role of different natural and anthropogenic factors of time and space under the formation of structure, functioning and succession of large river ecosystems.
Practically all types of water ecosystems, water flows of various size, small and large reservoirs, steppe and mountain lakes, bogs are presented in the Ob basin. The typisation on hydrophysical, hydrochemical and hydrobiological parameters of different types of lakes of the Upper Ob basin and Ob-Irtysh interfluvial area was made: Lake Teletskoye, Lake Gorkoye-Peresheechnoye, Lake Kulundinskoye, Lake Kuchuk and channels adjacent to them; the natural and anthropogenic factors determining water quality of ecologically different sites of large Ob river system with Aley and Barnaulka inflows have been characterised.
The research of spatial – temporal non-uniformity of taxonomic structure, phyto- and zooplankton development level, contents of chlorophyll “‡” simultaneously with vertical profiling by means of hydrologic STD-12 and SBE 25-01 SEALOGGER CTD probes allowed us to support the hypothesis on a prevailing role of hydrodynamic and hydrothermal factors in limiting plankton communities development in Lake Teletskoye.
A determining role of morphometry, altitude arrangement of water body and intensity of external water exchange in the formation of composition and structure of phyto- and zooplankton, zoobenthos and high water plants was established in the Novosibirsk reservoir. To estimate the degree of alive organisms participation in self-purification processes of water body the coefficients of heavy metals accumulation in hydrobionts of Novosibirsk reservoir were determined. The coefficients of accumulation in zooplankton can be arranged in the following order: Hg > Co > Mn > Be > Cd > Pb > Zn > Ni > Cu > Ba > V > As.
For estimation of factors of the formation and functioning of aquatic ecosystems the estimation of acute and chronic toxicity with the use of Daphnia, luminous bacteria and genotoxicity using barley root tissue, various objects of the environment surface water of rivers, lakes and reservoirs; some pollutants (pesticides, surface-active substances) was made.
Cytogenetic research of the Upper Ob basin water bodies and streams allowed us to expand the species lists of benthic animals to establish some seasonal dynamics laws of benthos organisms number and biomass.
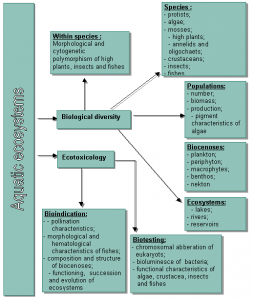
The project includes the investigations of the biological diversity of the Œb River basin and Œb-Irtish interfluvial area at various levels of biosystem organisation and ecological water objects state estimation (Fig. 1). It is proposed to investigate the following objects: river ecosystems of various types (Ob with inflows, Aley, Chulym, Tom, Inya), Lakes (Teletskoye, the lakes of Ob-Irtysh interfluvial area and Upper-Chulym), Novosibirsk reservoir and cooling-reservoirs of thermal power stations.
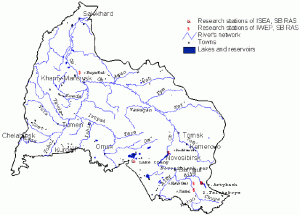
The institutes possess research stations on Lake Teletskoye, Novosibirsk reservoir and Lake Chany, low Ob (Karym-Kary) (Fig. 2).
Research plan: approaches and methods
The methodological basis is a system analysis. The methodical approaches include long-term observations, comparative analysis, experiments and modelling of processes. The use of standard field and laboratory hydrophysical, hydrochemical, hydrobiological, biochemical, cytogenetic, karyological, physiological and paleological methods is proposed. Analysis of the results obtained using standard and special mathematical methods application as well as geographical analysis.
Expected results
- Characteristic of biodiversity on genetic, population, biocoenotic and ecosystem levels; materials for establishment of biogeographical laws of aquatic flora and fauna origin and formation.
- Characteristic of yearly and long-term dynamics of taxonomic structure, number and biomass, phyto- and zooplankton, zoobenthos and macrophytes, fish and parasitic cenoesis spatial distribution; estimation of heterogeneity of spatial distribution of vegetative and animal organisms including basis empirical-statistical descriptive models.
- Parameters of intensity, direction and the ratio of production and destruction processes, elements of ecosystem biotic balance; estimation of their current state and factors of the formation of surface water quality in the basin; the maps of the ecological state of water objects in the basin.
- Lists of plants and animals species, being indicators in relation to pollutants entering the water bodies and streams; regional bioindicator systems developed on their basis.
- The program complex for mathematical processing of natural data, accumulation, systematisation and processing of the results of hydrobiological research, calculation of water quality integrated parameters and their cartographical display.
- The typological characteristic of the Ob basin water objects on hydrophysical, hydrochemical and hydrobiological parameters; estimation of the relative importance of natural and anthropogenic factors determining water quality of ecologically different sites of large river system and its catchment; the substantiation of the recommendations on ecological monitoring using parameters of biodiversity and measures on preservation and restoration of biological resources.
List of publications of participants related to the project
-
Vasiliev O.F., Kirillov V.V., lerkx J., Selegei ¬.¬. Kompleksnie issledovania Teletskogo ozera // Gydrologicheckie i ecologocheckie processi v vodoemach i ich vodosbornich basseinach.- Novosibirsk: SO RAN, 1995. ñ S.120-122. ñ (in Russian).
-
Egorkina G.I., Zarubina E.J. Ecologicheskii monitoring vodoemov s ispolzovaniem citogeneticheskich characteristic visshich vodnich rastenij // Regionalnoe prirodopolzovanie i ecologicheskii monitoring. ñ Barnaul, 1996. ñ S. 239. ñ (in russian).
-
Kiknadze I.I., Shilova A.I., Kerkis I.E. i dr. Kariotipi i morfologia lichinok tribi Chironomini. Atlas. Novosibirsk: Nauka, Sib. otd-nie, 1991. ñ 115 s. ñ (in Russian).
-
Kiknadze I.I., Butler M.G., Aimanova K.G., Gunderina L., Cooper K. Geographic variation in polytene chromosome banding pattern of the Holarctic midge Camptochironomus tentans (Fabricius) // Can. J. Zool. ñ 1996. ñ π 74. ñ P. 171-191.
-
irillov V.V., Chaikovskaya “.S. Sravnenie vidovogo sostava i obilija fitoplanktona vodotokov Ë vodoemov bassejna r. Chulim s primeneneim mer vkluchenija // Voprosi gidrometeorologii Vostochnoj Sibiri. ñ M.: Gidrometeoizdat, 1991. ñ S. 105-125. (in Russian)
-
Kirillov V.V., Shur L.¿., Ãitrofanova ≈.J., Ãitsukova L.D., Rudneva L.V., Zarubina ≈.J., Vesnina L.V., Dombrovskaja I.¿. Bioindikatsia kachestva poverchnostnich vod basseina r.¿ley // Jadernie ispitania i zdorovje naselenia ¿ltaiskogo kraja. ñ Barnaul: Izd-vo ¿ltaiskogo gos. un-ta, 1993. ñ S. 104-117. (in Russian)
-
Kirillov V.V., Kim G.V., Mitrofanova E.Yu., Zarubina E.Yu., Biesboer D. Algal and Macrophyte Communities of the Deepest Lake in Western Siberia, Lake Teletskoye // People, Lakes and Land: puzzling relationships (Abstr. to 16-th Intern. Symp. on Lake, Reservoir and Watershed management) Minneapolis/St Paul, Minnesota, 1996. ñ P. 92
-
Kirillov V.V., Kiknadze I.I., Rudneva L.V., Vesnina L.V., Egorkina G.I., Ãitrofanova ≈.J., Zarubina ≈.J., im G.V., irillova “.V., Çtveeva Œ.V. Biologicheskoye raznoobrazie vodnich ecosistem bassejna Verchnej Œbi // Œbskoj vestnik. ñ 1997. ñ N 2-3. ñ S. 51-57. (in Russian)
-
Kirillov V.V., Ãitrofanova ≈.J., Skabichevskaja N.¿., irillova “.V., im G.V. Paleoecologicheskie signali algotsenozov ecosistem ozer i ich vodosbornich bassejnov // Problemi rekonstruktsii klimata i prirodnoj sredi golotsena i Plejstotsena Sibiri. ñ Novosibirsk: Izd-vÓ In-t‡ archeologii i etnografii SO R¿N, 1998. ñ S. 222-233. (in Russian)
-
Çk‡rchenko ≈.¿., Rudneva L.V. Obzor chironomid (Diptera, Chironomidae) Gornogo ¿ltaya // Tschivotnij mir ¿ltae-S‡yanskoj gornoj strani. ñ Gorno-Altaisk, 1994. ñ S. 83-88. (in Russian)
-
Papina T.S., Vasiliev O.F., Eyrich S.S., Sukhenko S.A. Mercury in the Katun river: a case study of a naturally polluted system // Proc. of NATO ARW Global and regional mercury cycles: sources, fluxes and mass balances, Novosibirsk, Russia, 1995, Kluwer Academic Publishers, p.273-284, 1996.
Fig. 1. Structure of research of ecosystem biodiversity and ecological state estimation of the Ob basin and Ob-Irtysh interfluvial area water objects.
Fig. 2. Scheme of the Ob basin and Ob-Irtysh interfluvial area with the notes of scientific stations arrangement.