Limnological Insitute, SB RAS, Irkutsk
Head of the Institute:
Mikhail A.Grachev, Corresponding Member of RAS, Profeccor
P.O. Box 4199, Irkutsk-33, 664033, Russia
Tel.: (3952) 460504
Fax: (3952) 460405
email: info@lin.irk.ru
Principal researchers:
Ye.V.Likhoshway, Dr. LIN RAS SB, Irkutsk, Russia
G.I.Popovskaya, Professor LIN RAS SB, Irkutsk, Russia
Œ.I.Belykh Dr. LIN RAS SB, Irkutsk, Russia
A.I.Tanichev, Dr. LIN RAS SB, Irkutsk, Russia
“.¿.Sherbakova, LIN RAS SB, Irkutsk, Russia
S.I.Genkal, Professor Institute of Biology of Inland Waters,
RAS, Borok, Yaroslavl, Russia
R.Crawford, Dr., Alfred Wegener Intstitute for Polar and Marine Reseach, Bremerhaven, Germany
R.Jahn, Dr. Botanical Museum, Berlin, Germany
D.Lazarus, Dr. Museum of Natural History, Berlin, Germany
Project objectives
The purpose of the present project is evaluation of the species diversity of planktonic microalgae of Lake Baikal by a team consisting of Russian and European scientists. Expected results are the following: (i) a list of speacies of plaktonic microalgae of Lake Baikal; (ii) a collection of specimens of micralgae of Lake Baikal according to international standards having a official status; (iii) a computer database on the diversity of species of planktonic microalgae of Lake Baikal including sequences of some of their genes.
Evaluation of the diversity of species will include a review of the diversity in the past and analysis of biodiversity at present. The collection and the database will be structured in such a way that it could serve to detect changes of biodiversity in the future.
Background and significance of objectives
An important reason for the inclusion of Lake Baikal into the List of World Heritage of UNESCO was its unique endemic complex of aquatic organisms. Lake Baikal appeared ca. 25 mln. years before present. It was not covered by ice sheets during global glaciations. Its long existence as a deep, isolated water body resulted in evolution of the microflora which gave rise to the modern complex including endemic species as the dominating algae.
Conservation of the biodiversity of Lake Baikal is an important task which can be solved on the prerequisite that we know the biodiversity of the present – if we are going to protect biodiversity, we have to know what in particular has to be protected. A major part of the extant phytoplankton of Lake Baikal are endemic organisms (Meyer, 1930; Popovskaya, 1991). An inventory of biodiversity should include a list of species, keys which make it possible to identify species, data on their morphological variability and data on their annual and seasonal dynamics.
A huge amount of information has been collected up to this date on the biodiversity of the phytoplankton of open Baikal. A few lists of species have been published. Data of long-term observations on the seasonal and annual dynamics of the phytoplankton of Lake Baikal have been obtained. A few new species have been described. Morphology of some of these species has been studied in detail by means of electron microscopy. Variability of the ultrastructural features of the leading species has been studied by quantitative methods. Data on the biodiversity of phytoplankton of Lake Baikal have been collected during more than 150 years, beginning from the first publication by a German scientist Ehrenberg of 1843. However, evaluation of this biodiversity for the practical purpose of its conservation still remains a difficult problem.
First of all, the published lists of phytoplankton of Lake Baikal have to be reconsidered because some algae received new names and systematic positions. A few specie were identified erroneously, because only light microscopy was applied (e.g. Nitzschia acicularis).
Secondly, there is no modern atlas or treatise summarizing new data on the structure of planktonic algae of Lake Baikal and new data on their taxonomic position, and biologists have to use the monograph of Skabichevskiy published in 1960 – the numerous data of different authors concerning systematics, taxonomy and morphology of planktonic algae of Lake Baikal are scattered in papers published in different journals and brochures. These data have to be united into a single monographic survey. Moreover, it is necessary it revise some systematic groups of planktonic algae of Lake Baikal, because new important publications on the general systematics and taxonomy of algae appeared (Diatomovie vodorosli SSSR 1988, 1992; Krammer, Lange-Bertalot, 1988, 1991; Round, Crawford, Mann, 1990; Krammer, 1991a, 1991b, etc.)
Thirdly, it is impossible to compare specimens of algae which were collected recently with those described earlier, because there is no archive or collection of permanent preparations of planktonic algae of Lake Baikal which is available to the international scientific community.
Hence, evaluation of the biodiversity of planktonic algae of Lake Baikal, as part of quantitative evaluation of the diversity of its unique flora and fauna in general is an important problem. An advantage of the present project is the proposed close co-operation with curators of the oldest European collections of microalgae, which has already yielded promising preliminary results.
Research plan: approaches and methods
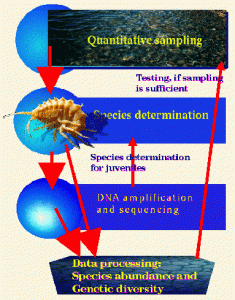
Methods of electron and light microscopy; epifluorescent microscopy; cultivation of microalgae; methods of molecular biology and DNA sequencing, including amplification and sequencing of DNA obtained from individual algae cells; computer data bases.
Expected results
- A library of reprints of papers concerning those groups of algae, representatives of which occur in the plankton of Lake Baikal (ca. 500 publications), especially of the first ones published in XIX century in Germany, because these old papers are the basis of modern systematics.
- Publication of a comprehensive lists of species of planktonic algae of Lake Baikal reflecting its biodiversity, and supplemented by a comparison with the earlier lists. Publication of the lists of dominating planktonic algae species of the different regions of the lake supplemented by data on the peculiarities of their environment.
- Evaluation of the diversity of species of picoplankton of Lake Baikal using samples which have been earlier collected monthly in different regions of the lake, and strains introduced into laboratory cultures (ca. 40 strains).
- Creation of an archive of permanent preparations of planktonic diatom algae collected in different regions of Lake Baikal since the 1960-es (ca. 1000 samples), and of a collection of algae preserved in media which do not destroy DNA. Both collections will be available to the international scientific community.
- Creation of a computer database which includes a list of species of planktonic algae of Lake Baikal, diagnoses and keys for their identification, illustrations, and DNA sequences. A computer data base on the distribution and abundance of planktonic algae species of Lake Baikal embracing the last forty years.
List of publications of participants related to the project
-
Popovskaya G.I. Lake Baikal. – The phytoplankton of Lake Baikal. In : Problems of Lake Baikal Lake, Novosibirsk: Nauka, 1978, 716 (36): 158-169.
-
Genkal S.I., Popovskaya G.I. On the systematic position of Stephanodiscus dubius subsp. Sibirica Skabitsch. – Information Bulletin. Biology of Internal Waters.. Leningrad: Nauka, 1984, 64, 7-10.
-
Mikhailov V.I., Popovskaya G.I. On the fine structure and ecology of Nitzschia acicularis from the phytoplankton of Lake Baikal and Selenga River – Izvestiya Sibirskogo Otd. AN SSSR. Ser. Biol. Novosibirsk: Nauka, 1986, 2, 54-57.
-
Popovskaya G.I. The history of investigation and the major results of studies of the phytoplankton Lake Baikal. In: The route of studies of Lake Baikal. Novosibirsk: Nauka, 1987, 199-210.
-
Popovskaya G.I. Phytoplankton of the deepest lake on earth. – In: Marine and freshwater plankton. Trudy Zool. Inst. Leningrad: Nauka, 1987, 172, 107-115.
-
Genkal S.I., Popovskaya G.I. Œn the fine structure of the frustules of Cyclotella minuta (Skv.) Antipova. – Information Bulletin. Biology of Internal Waters.. Leningrad: Nauka, 1990, 87, 21-26.
-
Genkal S.I., Popovskaya G.I. A new representative of Stephanodiscus Ehr. (S. binderanus (Kuetz.) Krieg. var. baicalensis Popovsk. Et Genkal var. nov.). – Information Bulletin. Biology of Internal Waters.. Leningrad: Nauka, 1990, 87, 21-26.
-
Genkal S.I., Popovskaya G.I. Peculiarities of the morphology of spores and auxospores of Aulacoseira islandica (Bacillariophyta). – Information Bulletin. Biology of Internal Waters.. Leningrad: Nauka, 1990, 89.
-
Genkal S.I., Popovskaya G.I. New data on the morphology of Aulacoseira islandica (Bacillariophyta). – Diatom Res., 1991, 6 (2), 255-266.
-
Genkal S.I., Popovskaya G.I. New data on the morphology of Aulacoseira baicalensis (K. Meyer) Sim. – Botanich. Zhur, 1991, 76 (2), 293-296.
-
Likhoshway Ye.V., Yakushin A.O., Puzyr A.P., Bondarenko N.A. Fine structure of the velum and girdle bands in Aulacoseira baicalensis. – Diatom Research, 1992, 7 (1), 87-94.
-
Tanichev A.I. Morphology of chrysomonades Spumella termo (Mueller) Hanel and S. gregaria sp.n. of Lake Baikal – Zool. zhur, 1993, 72(1), 23-29.
-
Likhoshway Ye.V., Kuzmina A.Ye., Potyemkina T.G., Potyemkin V.L., Shimaraev M.N. The distribution of diatom algae near a thermal bar in Lake Baikal. – Journal of Great Lakes Research, 1995, 22 (1), 5-14.
-
Tanichev A.I., Bondarenko N.¿. Free-living ciliates. – In : Atlas and keys of the pelagobionts of Lake Baikal (Œ.¿. Timoshkin, ed. ). Novosibirsk: Nauka, 1995, 146-181.
-
Babanazarova O.V., Likhoshway Ye.V., Sherbakov D.Yu. On the morphological variability of Aulacoseira baicalensis and Aulacoseira islandica (Bacillariophyta) of Lake Baikal. – Phycology, 1996, 35 (2), 31-41.
-
Sherbakova “.¿., Kirilchick S.V., Likhoshway Ye.V., Grachev Ã.¿. Phylogenetic position of diatom algae of the Aulacoseira genusfrom Lake Baikal as revealed by the nucleotude sequences of a fragment of the 18SrRNAgene. Molekulyarnaya biologiya 1998, 32 (4): 735-740.
-
Konstantinov Yu.M., … Belykh O.I., … Investigation of the gene of superoxide dismutase of different strains of cyanobacteria of Lake Baikal by methods of genetic engineering. -In: Problems of the conservaton of biodiversity. Novosibirsk.: Nauka, 1998, 29-30.
-
Lazarus D., Jahn R. Using the Ehrenberg collection. – Diatom Res., 1998, 13 (2): 273-291.
-
Crawford R.M. & Likhoshway Ye.V. The velum of species of Aulacoseira Thwaites. – Proc. of 15th Diatom Symposium, 1998, in press.
-
Grachev Ã.¿., … Belykh O.I., … Likhoshway Ye.V., Sherbakova “.¿. Limnological research on Lake Baikal in 1987-1998. In : Academic science in East Siberia. Novosibirsk: Nauka, 1999, 161-182.
-
Crawford R.M. & Likhoshway Ye.V. The frustule structure of holotype material of Aulacoseira distans (Ehrenberg) Simonsen. – Diatom Research, 1999, in press.
-
Sherbakova T.A., Rubtsov N.B., Likhoshway Ye.V., Grachev M.A. Combined ultrastructural studies and PCR with individual diatom algae cells. – Diatom. Res., 1999, in press.
-
Belykh O.I. et al. An eukaryotic alga from the picoplankton of Lake Baikal: morphology, ultrastructure and rDNA sequence data. – Hydrobiologia, 1999, in press.
-
Belykh O.I., Zaika ≈.I., Berezikov ≈.V. Autotrophic picoplankton of Lake Baikal. – Sibirskiy eklogicheskiy zhur. 1999, in press.
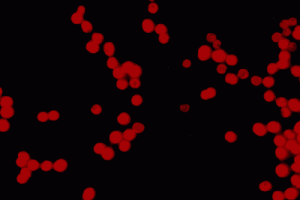
Epifluorescence microscopy. Autofluorescence (red fluorescence) of picocyanobacterial cells of strain Synechocystis sp., BAC 9721 under green excitation. X 1250.
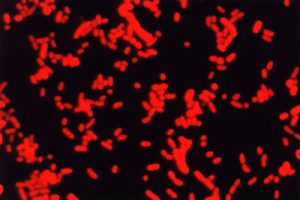
Epifluorescence microscopy. Cells of picocyanobacteria of strain Synechococcus sp., BAC 9818. X 1250.
Epifluorescence microscopy. Cells of picocyanobacteria of strain Synechococcus sp., BAC 9808 under green excitation. X 1250.
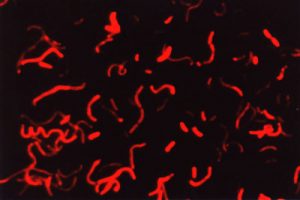
Epifluorescence microscopy. Autofluorescence (red fluorescence) of picocyanobacterial cells of strain Synechococcus sp., BAC 9807 under green excitation. X 1250.